It has become very important to have a well-balanced and properly functioning immune system for the maintenance of human health. The term immunity defines body’s natural defence system against a vast array of diseases and disorders. Change in the body’s immune system, caused by agents that activate or suppress its function are called Immunomodulators. There is also a common perception among the rank and file of the population that immunity can be “boosted” by consuming nutritional supplements. The “immune boosters” segment includes vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, probiotics, and “functional foods” as well as other approaches. This has a huge commercial impact, with the global market of dietary supplements estimated around 133 billion USD.
Our immune system is often conceptualized as possessing two principal components: innate and adaptive immunity, which work in concert to defend the body against infection. The innate system is ancestral and present in invertebrates as well as vertebrates and does not respond to environmental changes. The innate system reacts directly to a wide variety of invading pathogens. Indeed, the cells of the innate immune system represent the first line of defence in the immunosurveillance network. The primary cells involved in the identification and spontaneous killing of offensive targets (virus-infected cells, tumor cells, bone marrow stem cells and embryonic cells) are the natural killer (NK) cells, which originate from the bone marrow and travel in a unidirectional and almost exclusive way to the spleen.
In contrast, the adaptive system, also termed specific immunity, is acquired through interactions with the environment. Adaptive immune responses are central to the body’s ability to eliminate bacterial, viral and parasitic infections. Adaptive immune responses are carried out by white blood cells called lymphocytes which are of two broad classes called B cells and T cells. The innate and adaptive systems are highly integrated and interdependent. In addition to being a requisite for adaptive immunity, the innate system is responsible for the early killing and clearance of infectious pathogens and the resolution of the inflammatory response. The most important means by which the immune system communicates internally and externally is through the use of cytokines, small soluble signalling molecules. Cytokines play a crucial role in the selection, initiation and modulation of an appropriate immune response. The immune system can give rise to several disorders when it is weakened or over-activated.
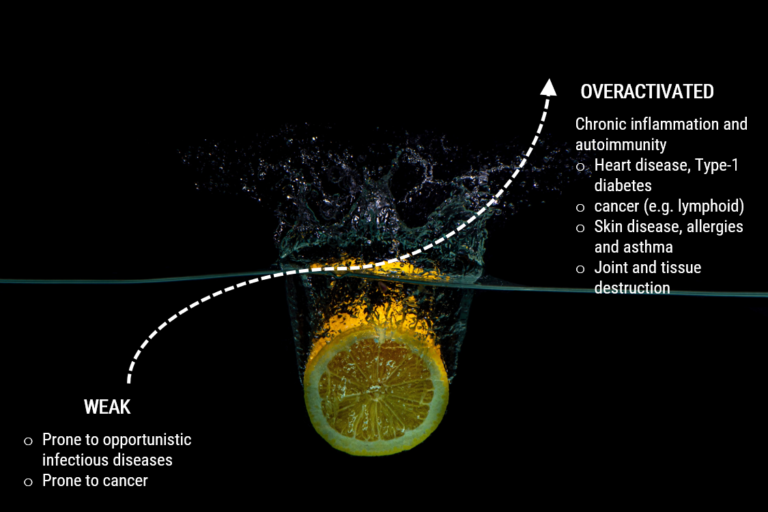
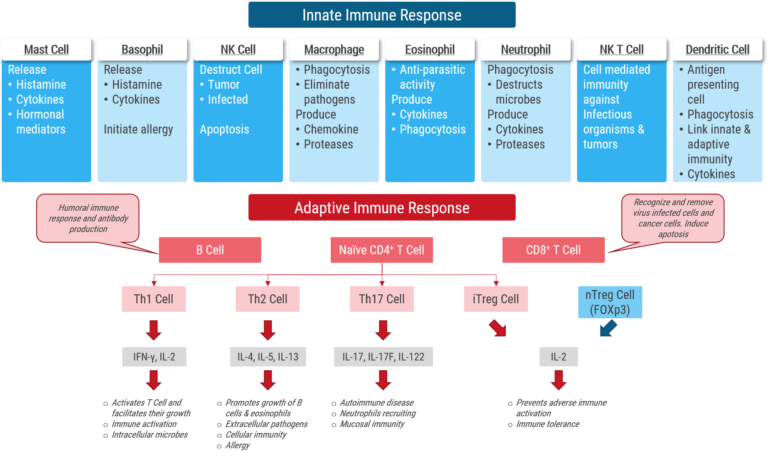
Understanding the action of botanical ingredients on immune responses would call for a brief discussion on the components of the immune system. Natural products otherwise referred to as botanical ingredients or phyto-pharmaceuticals have been discovered to play an important role in the regulation of immune function. They control the immune system in a pleiotropic manner (stimulation of genetic action in a cascading effect) and participate in various processes of the adaptive/innate immunity. The function of adaptive immune responses is to destroy invading pathogens and any toxic molecules they produce. In humoral immune responses of the adaptive system, B-cells (bone marrow derived) are activated to secrete antibodies, called immunoglobulins. The antibodies circulate in the bloodstream and permeate the other body fluids, where they bind specifically to the foreign antigen that stimulated their production. Binding of antibody inactivates viruses and microbial toxins (such as tetanus toxin or diphtheria toxin) by blocking their ability to bind to receptors on host cells. Antibody binding also marks invading pathogens for destruction, mainly by making it easier for phagocytic cells of the innate immune system to ingest them. In cell-mediated immune responses, activated T-cells (thymus derived) react directly against a foreign antigen that is presented to them on the surface of a host cell. The T-cell, for example, might kill a virus-infected host cell that has viral antigens on its surface, thereby eliminating the infected cell before the virus has had a chance to replicate. In other cases, the T-cell produces signal molecules that activate macrophages to destroy the invading microbes. So botanical ingredients have stimulatory effect on humoral and cell-mediated immune response, stimulate humoral response by acting at various levels of immune mechanism such as antibody production, release of mediators of hypersensitivity reactions and tissue responses to these mediators in the target organs. Therefore, natural products have great potential as targeted immune modulators. In fact, based on proper understanding of various immunomodulatory activities of each ingredient, lead immunomodulatory molecules for future therapeutic use can be designed.
The current situation relating to the Covid-19 viral epidemic has stimulated research to develop plant-derived natural products or botanical ingredients as potent and safer leads to act as immunomodulators. In recent years, use of medicinal plants is gaining wide recognition due to their versatility, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Newer generation of botanical ingredients have been developed and marketed to modulate the complex immune process in such a way so as to prevent the infection rather than treatment or cure of the disease. However, it must be noted that the immune system carries out its important defensive function in intimate and coordinated interaction with the nervous and endocrine systems. In addition, it is generally recognized that a great effort should be placed on the standardization of methods used to study immune modulation by Botanical ingredients. In terms of formulations, this also includes a standardization of the preparations themselves. One of the greatest inconsistencies of clinical research related to immunomodulatory botanical ingredients are caused by the lack of quality control of the source materials used. Formulations based on botanical ingredients may be therefore recommended for use as positive immunomodulators. There are several botanical products with potential therapeutic applications because of their high efficacy, low cost and low toxicity.
References are available on demand and constitute internal knowledge repository of Consytel Life Sciences Pvt Ltd.
© Consytel 2025. Powered by WordPress
